Contact Kulzer International

GLUMA® Desensitizer
More gain, less pain.
One of the most impairing effects on your patients’ daily well-being is hypersensitivity. Sweet or sour dishes, hot or cold morsels – the acute pain is unpleasant and rather blocked out.
For more than 20 years, one drop of GLUMA Desensitizer has been all you need to stop and prevent hypersensitivity. The result is fast and effective, without mixing, curing or repetitive steps. And your patients feel a prompt relief.
Benefits
GLUMA Desensitizer can be used under every restoration – direct and indirect – to ensure your patients the comfort they deserve.
- One-step placement
No agitation or light curing required makes it easy to use and saves time. - Universally compatible
GLUMA Desensitizer can be used with bonding and restorative materials, in any situation. - Economical
One drop, multiple applications.
Good to know
Indications
- To reduce or even eliminate pain in exposed cervical areas not requiring restoration.
- To alleviate or prevent dentinal sensitivity after preparation of teeth to receive indirect or direct restorations.
Applications
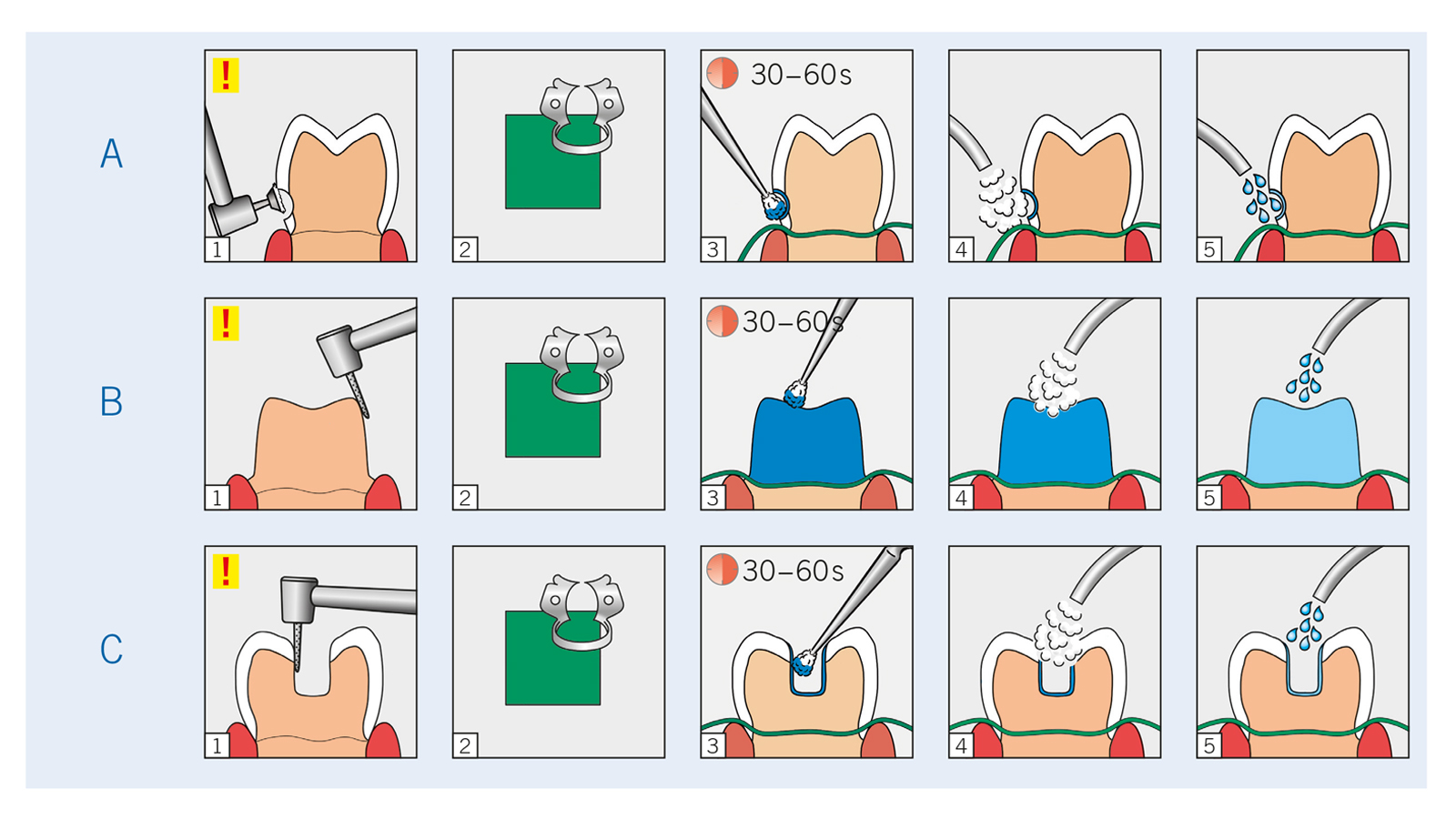
Application Guide
Science
How it works
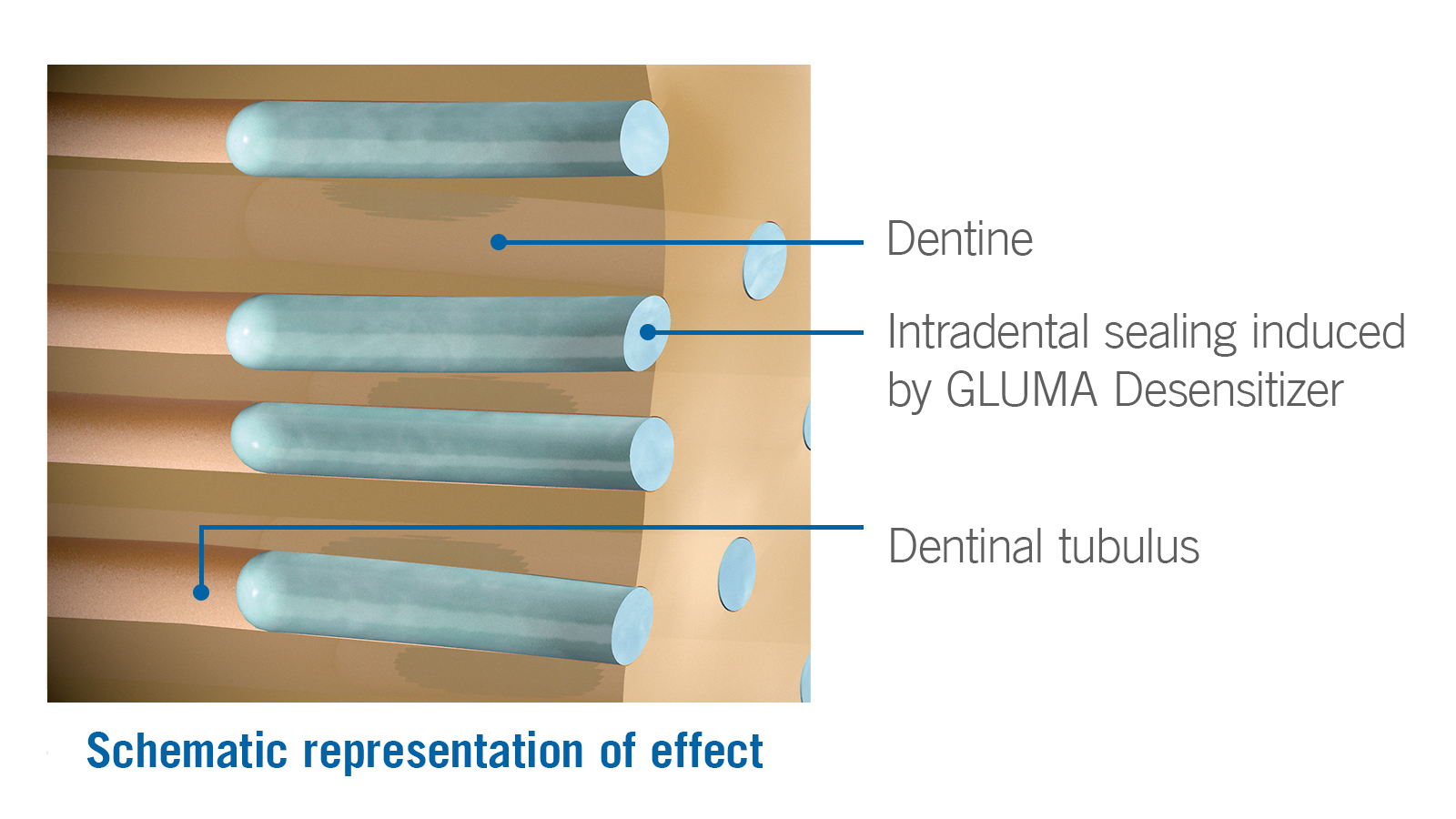
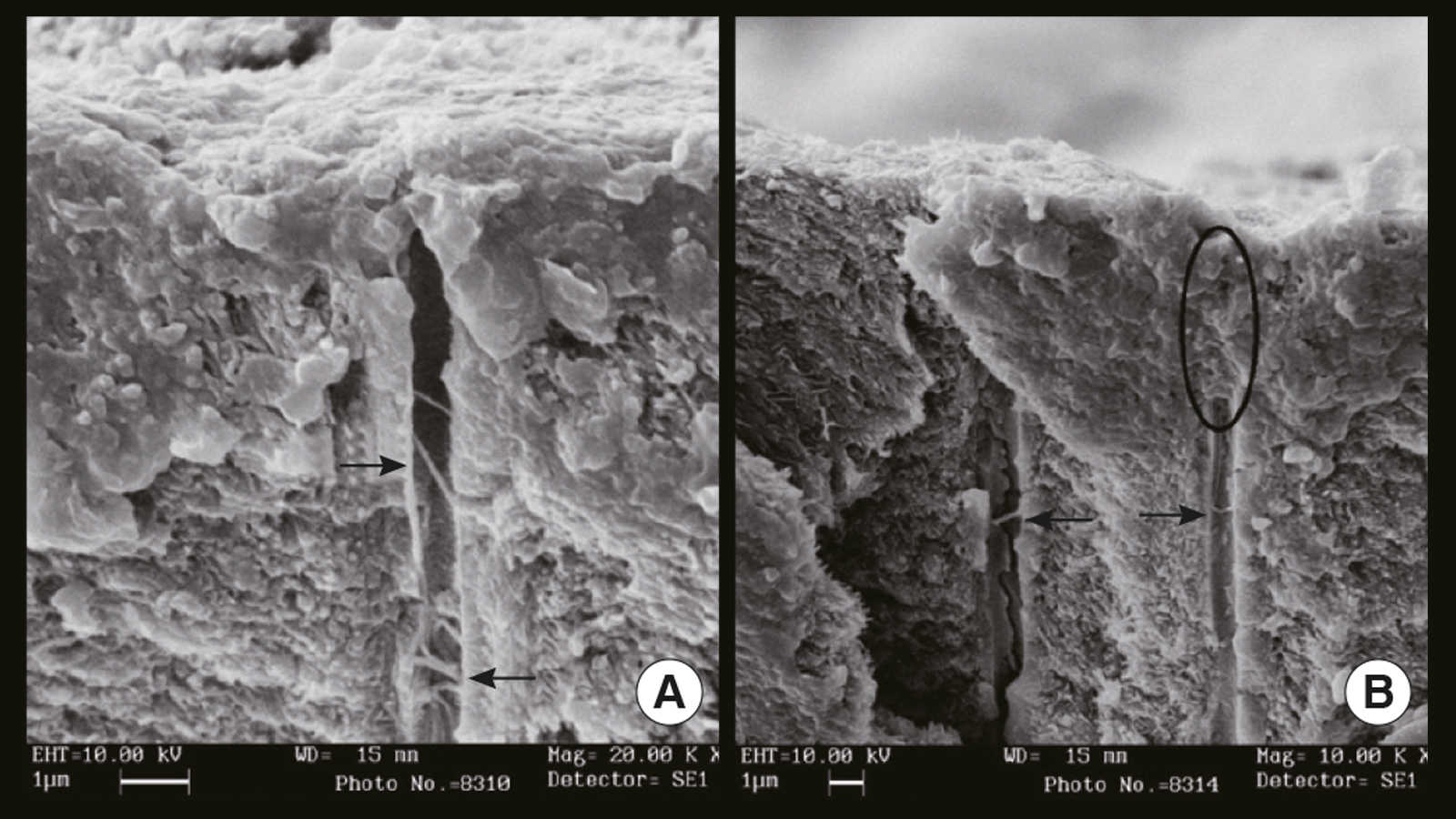
- GLUMA Desensitizer achieves its effects by precipitation of plasma proteins, which reduces dentinal permeability and occludes the peripheral dentinal tubules.
- This inhibits the flow of fluid through the tubules which is the cause of sensitivity.
- In addition, GLUMA Desensitizer provides a seal that acts as a microbial barrier.